Two new research projects have emerged from the original Phyto-V data
- The Covid Vaccine Nutritional Intervention Study
- The Peripheral Neuropathy nutritional intervention study
The Covid Vaccine nutritional intervention study
EudraCT number: 2021-002826-26
Background: A major study, published in the BMJ, shows that people with suboptimal gut health had significantly more side effects to the covid vaccine and were less likely to get a good immune protection from it. This supports evidence from the UK nutritional intervention study that older, overweight, sedentary people who eat more processed sugar, with a history of indigestion or taking medication for high BP were more likely to have poor gut health and more problems after covid...read more.
Several studies have suggested exercise around the time of the vaccine and certainly being generally physically active enhances a flu vaccine response. Likewise a recent systematic review and meta-analysis evaluated twelve scientifically randomised studies and reported that patients taking , mainly lactobacillus probiotics with prebiotics in supplements form, were found to have higher influenza hemagglutination inhibition antibody titres after vaccination. They concluded that concomitant prebiotics or probiotics supplementation with influenza vaccination may hold great promise for improving vaccine efficacy. Better vitamin D status has also been associated with greater seroprotective responses to vaccination following Influenza vaccination [Lee]. Vitamin D deficiency continues to be common across the UK, as recently confirmed in the UK Biobank cohort [Sutherland].
Purpose: The hypothesis for this double blind placebo controlled randomised trial is that lifestyle advice to promote gut health, supplemented by a lactobacillus probiotic, inulin prebiotic and Vitamin D in a capsule could enhance antibody titres post covid-19 vaccination compared to standard care. It is believed that higher antibody titres confers greater immunity against covid-19 exposure. Probiotic supplement can help gut health and the one chosen for the National covid vaccine support study was yourgutplus+ as the one most likely to help and had a excellent safety profile in the previous covid study.
Design: After written informed consent all participants will be randomised to a nutritional supplement containing 5 lactobacillus probiotic strain, an inulin prebiotic and vitamin D3 or placebo (2:1) called Yourgutplus. This brand was chosen by the scientific committee as the one most likely to help and has a proven safety profile in the previous covid study. In the mean time, in summary we know that:
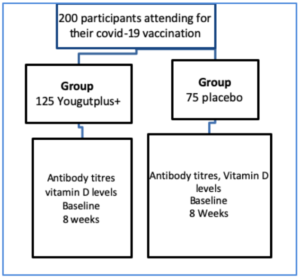
Both groups will also be given an information sheet to support verbal advice describing and advising the exercise, lifestyle and dietary changes which help promote health gut flora. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike antibody titres will be measured at 4 weeks and 2 months in each randomised group using the Roche Elecsys®. The primary statistical end points are the difference in antibody titres at baseline and 2 months between the two randomised groups. The secondary statistical end point is the levels of exercise and BMI recorded in all participants in relation to antibody titre. Any person contracting a confirmed covid infection post vaccination also will be asked to inform the trials unit.
Roche pharmaceutical have agreed to supply the antibody tests free of charge for this study. Up to March 2024 the trial recruited 55 participants and the target is 100. Until the results are available based on the background evidence, it would be very sensible to follow lifestyle strategies to improve gut health before and after the vaccine. There is already evidence that probiotics, vitamin D and exercise can reduce side effects and increase effectiveness of the flu vaccine.
The Peripheral Neuropathy nutritional intervention study
Peripheral neuropathy (PN) is a type of nerve damage that characteristically causes pins and needles, numbness coupled with a distressing sensation of burning known as hyperaesthesia a “stocking and glove” distribution. In more severe cases muscle weakness, impaired balance and coordination causing difficulty with movement and falls.
About 4% of the population of the UK are known to be affected by PN at any one time. That’s over 2 million people living in the UK with the distress of PN without any effective treatments being available for the majority. For many people, no underlying cause is found (idiopathic) but contributory factors include:
- Diabetes
- Alcohol abuse
- Vitamin B deficiency and mineral deficiencies
- Chemotherapy such as cisplatin, taxanes and vincristine
- Long covid
The underlying mechanisms of nerve damage is multifactorial but recently, scientific attention has focused on the contribution of oxidative stress and neuroinflammation. Both of these factors have been shown to accelerate spinal glial (nerve) cell degeneration and block repair of damaged nerves.
Phytochemicals, found in colourful fruit, vegetables and spices, have reported reduced markers of oxidative stress and inflammation which correlated with improved peripheral nervous system functional recovery in several laboratory studies. There are some suggestions of benefits in humans with PN but until now robust clinical studies have not been forthcoming. Recently, however, some intriguing information has been gained from a scientific study involving people suffering from long covid.
The Long covid study and peripheral Neuropathy
This study, completed last year, involved 147 people with multitude of distressing symptoms including 6% with peripheral neuropathy, pins and needles or hyperaesthesia. Fortunately, these troublesome neurological symptoms improved in response to the intervention which consisted of two nutritional supplements. The first aimed to improve gut health and vitamin D levels with a capsule called Yourgutplus. The second, called Phyto-V, boosted the intake of specific natural nutrients in plants called phytochemicals known for their anti-viral, anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative properties. In the final publication in the journal COVID, although these symptoms were noted, the emphasis was on the substantial improvements in fatigue, sleep, muscle aches, gut symptoms and overall wellbeing.
Since the trial completed, the trials unit started receiving emails from people across the world who had bought the supplements independently, letting them know that their long standing neuropathy had improved. For example, Rachael who took the time to email the trials unit, said:
media reports of the study. I was nicely surprised that after 4 weeks my long standing neuropathy started to improve. When I stopped it, my pins and needles returned. Happily, when I restarted it again they disappeared – I won’t stop now”
Following these comments and the results seen in the trial the trials team decided to look into the causes and treatments for PN in more detail. The scientific committee lead by a team from Bedford and Addenbrookes Cambridge University Hospitals was therefore re-convened and a new trial designed. Participants with PN will be randomised to either placebo, Yourgutplus, Phyto-V or both which will be repackaged so the patients won’t know what they will be taking. Likewise, the medical team will not know – a design technique called double blind which aims to reduce any unconscious bias between the two randomised groups.
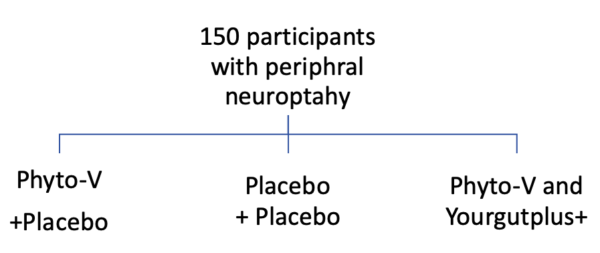
After 150 patients have finished the 6 month intervention, the blinding-codes will be cracked open and we will find, for sure, whether our suspicious are confirmed. We will also be able tell whether Phyto-V works on its own or whether it has to be combined with Yourgutplus as in the covid trial. This will be the largest and most robust nutritional intervention in the World addressing the discomfort of peripheral neuropathy and if positive could provide a practical, safe and low cost self-help strategy for millions.
More details of the study, its progress and eventual results can be found on the trial website (phyto-v.com) along with practical advice for people living with peripheral neuropathy.
